


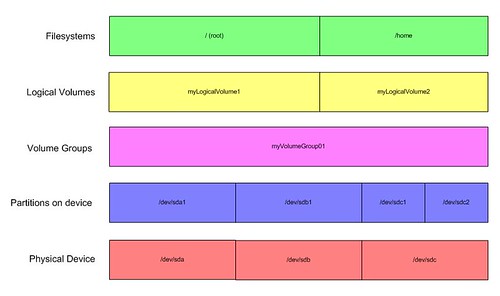
For example, FreeBSD uses /dev/adaX (where X is one or more digits) to refer to PATA disks and /dev/adaXpY (where X and Y are both one or more digits) to refer to partitions on PATA disks. Other Unix-like systems may refer to disks and partitions in other ways. Note that on PCs using MBR partitioning, due to the limit of four primary partitions and the way extended partitions are handled, the partition numbering can slightly differ from the actual partition count. For example, the device node files /dev/sda1 and /dev/sda2 refer to the first and second partition of the first PATA device. A number after the device letter signifies the number of the partition. Each partition will show up under /dev as a separate device node. If there are more than 26 such devices in the system, devices from the 27th onwards are labeled /dev/sdAa, /dev/sdAb and so on.Ī physical storage device can be divided into multiple logical storage units known as partitions. The prefix sd was originally used for SCSI devices, but is now used for all PATA and SATA devices, including devices on an IDE bus. In Linux prior to kernel version 2.6.20 the prefix hd signified an IDE device, so for instance the device files /dev/hda, /dev/hdb and /dev/hdc corresponded to the first, second and third IDE device respectively. Storage devices are labeled under /dev according to the type of device followed by a letter signifying the order in which they were detected by the system. In Unix-like operating systems, devices are represented by special file system objects called device nodes which are visible under the /dev directory. The term drive refers to a physical storage device such as a hard disk, solid-state disk, removable USB flash drive etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
